
This in turn increases the availability of NEFAs and glycerol for gluconeogenesis and a trend toward ketogenesis during stress. Another cAMP pathway is stimulated by epinephrine in adipose cells and enhances the activity of hormone-sensitive lipase.

This reduces the need for muscle cells to remove glucose from the blood and spares blood glucose for use by the nervous system during stressful times. Because glucose-6-phosphate resulting from glycogenolysis cannot be converted into free glucose and leave the muscle cell, it is used directly in glycolysis. Epinephrine activates adenylyl cyclase in muscle cells, resulting in increased glycogenolysis ( Figure 12-24). Carr Ph.D., in Vertebrate Endocrinology (Fifth Edition), 2013 1 Acute Stress and MetabolismĪn early response to stress is the elevation in epinephrine release from the adrenal medulla.
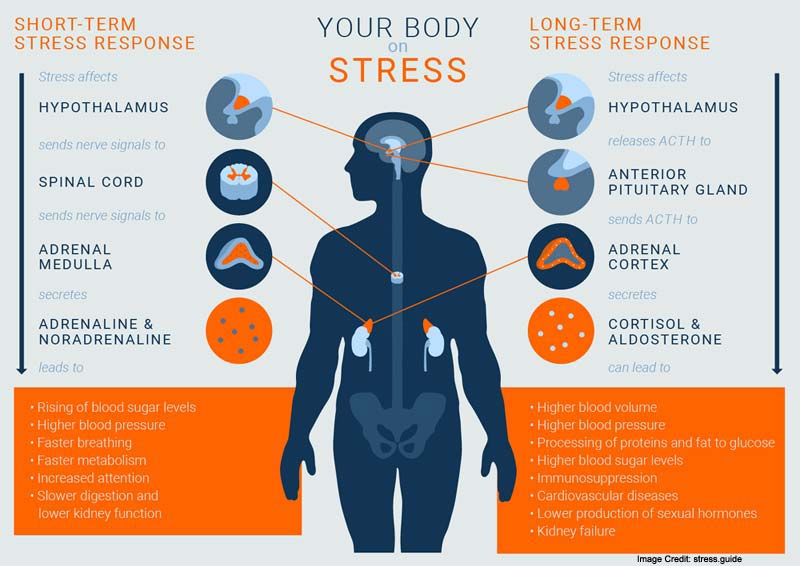
Consequently, the amount of epinephrine and norepinephrine released is usually carefully titrated to correspond to the severity of the stressor.ĭavid O. If too little response is released, the impact on target tissues will be insufficient too much release, however, is often fatal. Sympathetic activation is not an all-or-nothing response and the strength of the response can be modulated to the needs of the moment ( Romero and Wingfield, 2016). The amount released, however, is very important. Because the secretory cells are neurons, catecholamine release is very quick and effects can be seen in less than a second.Ĭatecholamines orchestrate the entire fight-or-flight response. When a stressor begins, epinephrine and norepinephrine are released from the adrenal medulla and norepinephrine is released from the sympathetic nerve terminals. The physiological responses in mammals and nonmammals, however, appear to be essentially identical ( Young and Landsberg, 2001). These cells are called chromaffin and are homologous to cells in the adrenal medulla of mammals. In these species, cells that release epinephrine and norepinephrine are embedded in the wall of the kidneys. Most nonmammalian species, however, lack a well-defined adrenal medulla. Another major source of norepinephrine is nerve terminals of the sympathetic nervous system. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are released from two different cell populations in the adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla is essentially a modified sympathetic ganglion where each secretory cell is a neuron without an axon ( Young and Landsberg, 2001). In mammals, epinephrine is primarily produced in the adrenal medulla – the center portion of the adrenal gland.

The location of epinephrine release depends in part on the species.

Michael Romero, in Encyclopedia of Animal Behavior (Second Edition), 2019 Anatomy


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
